Design thinking
- Performing a paradigm shift in the way we create solutions
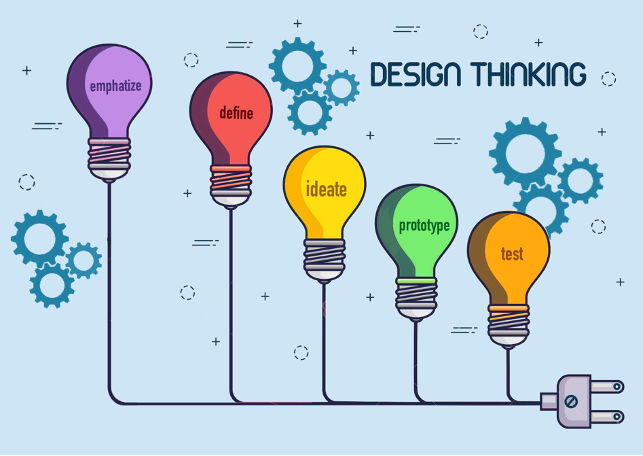
Design Thinking, a 5-stage design methodology, provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. This is especially useful in tackling complex problems that are ill-defined. With this methodology, managers and professionals will be able to design human-centric products and programs both for internal or external applications.
Objectives of Design Thinking:
- Describe the process, applications and key events in Design Thinking, thus enabling participants to integrate the methodology into their operations
- Identify users’ needs and wants by adopting the tools and techniques involved in empathizing with users
- Define a problem from users’ perspectives, framing a problem into a potential solution applicable to the users’ world and situations
- Generate solution ideas to meet users’ needs and wants using creative thinking techniques and tools
- Develop prototypes rapidly in order to identify potential shortfalls and opportunities for refinements
- Test a product for further enhancement and refinement
Sample Outline of Design Thinking:
-
Understanding Design Thinking
- What is Design Thinking?
- The 5-stage Design Thinking Model
- Advantages of a solution-based approach to problem solving
- Applications
- The iterative process
- Understanding the users’ world
- The “number 1 sin” of many designers
- The need to understand users’ world, experience and motivation
- Experience the users’ world
- How to understand users’ concerns
- Key questions to ask users
- Defining a problem
- The problem with traditional problem statements
- Defining a problem from users’ perspective
- From empathy to problem definition
- Benefits of a human-centered problem statement
-
Ideation
- The need to think out of the box
- Principles of creative thinking
- There are more ways to think than just doing brainstorming
- Some tools in generating creative ideas
- Let your creative juice flow
-
Prototyping
- Rapid prototyping
- Benefits of multiple prototypes
- Testing a prototype
- Making adjustment, improvement and refinements
- Testing
- Formative and summative evaluations
- Why rolling out is not an end?
- Developing a test check-list
- How to test a solution?
- The iterative process
Contact Talent Professional today for your best suited Design Thinking solution to drive your business to success in tacking complex issues and developing user-centric solutions!
Remarks: Program objectives and outlines are for reference only; programs would be tailor-made with clients' specific requirements.


